Retry pattern is a resilience strategy that automatically re-attempts a failed operation (such as a network call) a specified number of times, often with delays in between attempts, to handle transient errors gracefully. Anyone who has worked with microservices of reasonable complexity knows that failures are inevitable. In a distributed system, where multiple services communicate over the network, failures can occur due to various reasons such as network issues, service downtime, or unexpected errors. These failures can lead to a poor user experience if not handled properly.
Many of these failures are transient in nature—they might be temporary network glitches, momentary service overloads, or brief connectivity issues that resolve themselves quickly. However, if these intermittent failures are not handled properly, they can lead to a cascading failure, where one service failure causes other dependent services to fail as well. This can result in a complete system outage, leading to significant downtime and loss of revenue.
There are multiple resilience patterns that can be used to handle such failures. In this blog post, we will explore the retry pattern in detail and implement it using Spring Boot.
📚 For a broader overview of resilience patterns (including retry, circuit breaker, bulkhead, and more), check out our complementary guide:
Top Resilience Patterns in Microservices and implementing in Spring Boot
Before diving into the code, let's understand how the retry pattern works:
The retry pattern involves automatically retrying a failed operation with the expectation that it might succeed on subsequent attempts. This is useful for handling transient failures such as network blips or temporary service unavailability.
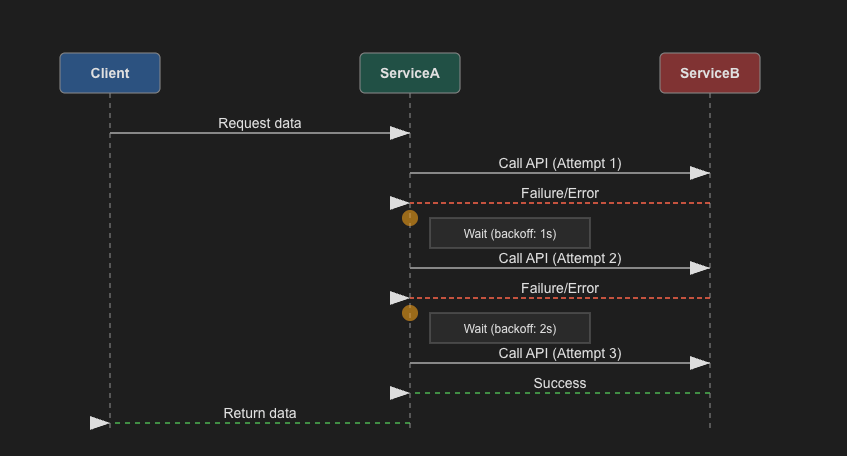
In the above diagram, the client sends a request to Service A, which in turn calls Service B. If Service B fails, Service A will retry the call after a back off period. The back off period can be exponential, meaning it increases with each failure.
Now that we understand the retry pattern, let's see how to implement it in a Spring Boot application.
In this blog we will follow the new resilience features introduced in Spring Framework 7.0. For version prior to 7.0, you can refer to the previous blog where we implemented the retry pattern using Spring Retry.
As of Spring Framework 7.0, the @Retryable annotation is part of the core framework, so you no longer need to add the spring-retry dependency.
To enable the processing of resilience annotations, you can declare @EnableResilientMethods on a corresponding @Configuration class.
@Configuration @EnableResilientMethods public class AppConfig { }
Let us say we have a method that fetches weather data from a weather API. We can annotate this method with @Retryable to enable retry functionality.
@Retryable(includes = IOException.class, maxAttempts = 3, delay = 100, jitter = 10,multiplier = 2) public WeatherRecords.WeatherData getWeather(PlaceRecords.Location location, String travelDate){ log.info("Getting weather data for location: {} and date: {}", location, travelDate); String uriString = UriComponentsBuilder.fromUriString("/forecast?lat=-{lat}&lon={long}&appid={apiKey}&units=metric") .buildAndExpand(location.latitude(), location.longitude(), apiKey) .toUriString(); var weatherResponse = weatherClient.get() .uri(uriString) .retrieve() .body(WeatherRecords.WeatherResponse.class); return weatherResponse.list().stream() .filter(weatherData -> weatherData.dtTxt().startsWith(travelDate)) .findFirst() .orElseThrow(()->new NoDataFoundException("No weather data found for the date",100)); }
In this code:
@Retryable annotation specifies that the method should be retried if it fails.includes specifies the exception types that should trigger a retry (in this case, IOException).maxAttempts specifies the maximum number of attempts (including the initial attempt), set to 3.delay specifies the initial delay in milliseconds before the first retry (100ms).multiplier specifies the multiplier for exponential backoff (2, so delays will be 100ms, 200ms, 400ms, etc.).jitter adds randomness to the delay to prevent thundering herd problems.This configuration will retry the method up to 3 times when an IOException occurs, with exponential backoff starting at 100ms and doubling with each retry.
RetryTemplate provides a programmatic API for retrying arbitrary blocks of code. We can use this to retry any code block that is not annotated with @Retryable.
var retryTemplate = new RetryTemplate(); retryTemplate.execute( () -> jmsClient.destination("notifications").send(...));
If you want to customize the retry logic, you can create a RetryPolicy and pass it to the RetryTemplate.
var retryTemplate = new RetryTemplate(RetryPolicy.withMaxAttempts(5)); retryTemplate.execute( () -> jmsClient.destination("notifications").send(...));
To stay updated with the latest updates in Java and Spring follow us on linked in and medium.
Learn about the top resilience patterns in microservices and how to implement them in Spring Boot. This guide covers circuit breakers, retries, timeouts, bulkheads, and more.
This guide explores the features and usage of the RestClient introduced in Spring 6, providing a modern and fluent API for making HTTP requests. It demonstrates how to create and customize RestClient instances, make API calls, and handle responses effectively.
Find the most popular YouTube creators in tech categories like AI, Java, JavaScript, Python, .NET, and developer conferences. Perfect for learning, inspiration, and staying updated with the best tech content.

Get instant AI-powered summaries of YouTube videos and websites. Save time while enhancing your learning experience.